Measurement Instruments
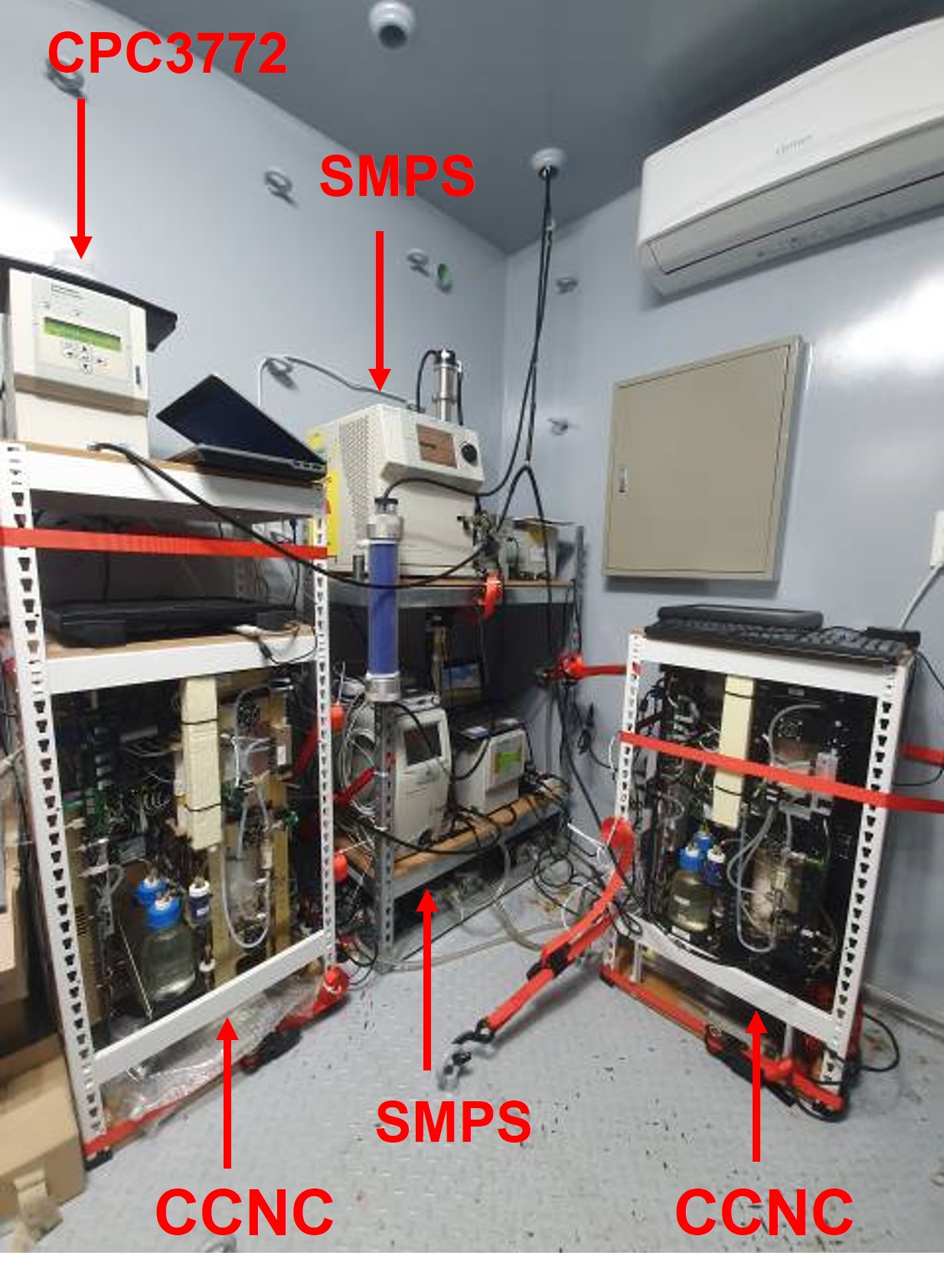
We measure aerosols and cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) with the following instruments.
1. Condensation particle counter (CPC)
– model : 3776 and 3772, TSI Inc., United States
– target : number concentrations of aerosols larger then 3 nm (model 3776), 10 nm (model 3772)
– resolution : 1 s.
ᅠ
2. Scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS)
– model : 3936L10, TSI Inc., United States
– target : number concentrations of aerosol by set size bins
– resolution : 3 min
– we usually set the size bin to 10-500 nm.
ᅠ
3. Cloud condensation nuclei counter (CCNC)
– model : CCN100, Droplet Measurement Technologies. United States
– target : number concentrations of CCN at a certain supersaturation
– resolution : 1 s
– we usually set supersaturation to 0.2%, 0.4%, 0.6%, 0.8% and 1.0%.
(For 0.2%, measuring time is 10 min, for the other, measuring time is 5 min.)
Measurement Regions
We have carried out many measurement campaigns in various regions (e.g., Seoul, Yellow Sea, Jeju island, Boseong Meteorological Observatory).
1. Seoul
– location : College of Science, Yonsei University (37.564°N, 126.935°E)
– period : 2005 – present (almost)
ᅠ
2. Yellow Sea (YES-AQ campaign)
– location : 35.43~37.23°N, 124.28°E
– period : 2018 – present (only springtime)
ᅠ
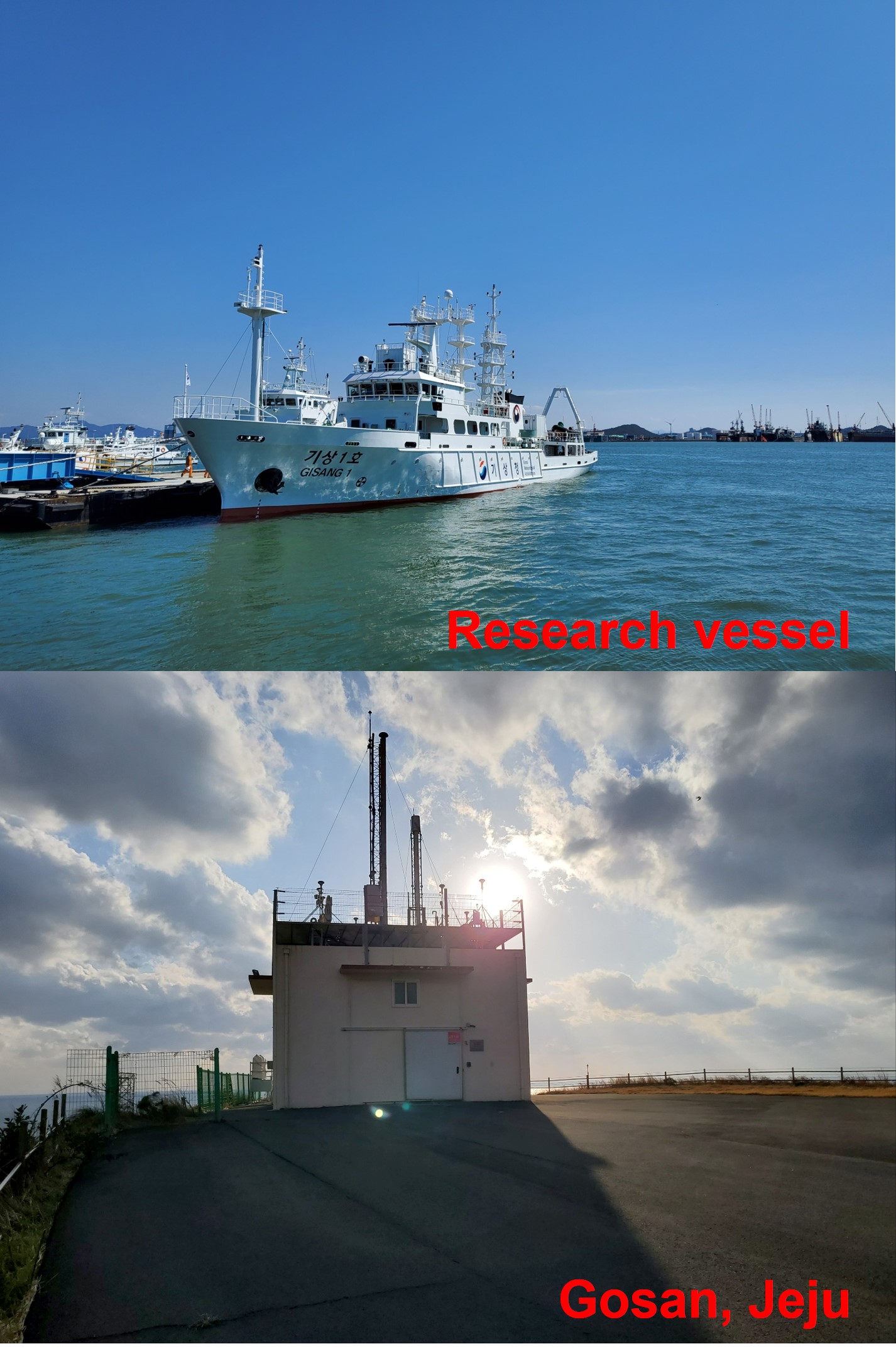
3. Jeju Island
– location : Gosan Station (33.293°N, 126.163°E)
– period :

Measurement Results

1. Variation of aerosol and CCN concentrations
Aerosol concentrations in Seoul tend to decrease steadily and show variations with a minimum in summer and a maximum in winter.

2. New particle formation
New particle formation (NPF) means the formation of molecular clusters from precursor vapors and their subsequent growth to larger sizes. According to Yu and Luo (2009), since at least 50% of aerosols in East Asia can be formed through NPF events, NPF is important phenomenon.
서울에서는 2018년부터 매년 NPF의 발생빈도가 증가하고 있으며, 평균 발생 빈도는 23.5%입니다.
서울과 서해에서의 NPF는 주로 낮은 온도와 습도, 높은 일사량과 풍속 조건에서 일어났습니다.

3. ???


1 Comment
Chanwoo Ahn · 2023년 02월 09일 at 9:51 오전
Amazing!